Embark on a journey through the realm of renewable energy technology, where innovation and sustainability intersect to shape our future. From harnessing solar power to tapping into wind energy, this topic delves into the cutting-edge technologies revolutionizing the way we power our world.
As we delve deeper into the various sources and technologies driving the renewable energy sector, a clearer picture emerges of the potential and possibilities that lie ahead in our quest for a greener planet.
Overview of Renewable Energy Technology
Renewable energy technology refers to the use of energy sources that are naturally replenished, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. These sources are considered sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.Renewable energy sources play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
They offer a cleaner and more sustainable way to meet the energy needs of today's world while minimizing the impact on the environment. By harnessing renewable energy, we can move towards a more sustainable and greener future.
Popular Renewable Energy Technologies
- Solar Power: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean and abundant source of energy.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines harness the power of the wind to generate electricity, offering a renewable and cost-effective energy solution.
- Hydropower: Hydropower plants use flowing water to produce electricity, making use of the Earth's natural water cycle.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal power plants utilize heat from beneath the Earth's surface to generate electricity, offering a reliable and sustainable energy source.
- Biomass Energy: Biomass is organic material that can be used to produce heat, electricity, and biofuels, providing a renewable alternative to fossil fuels.
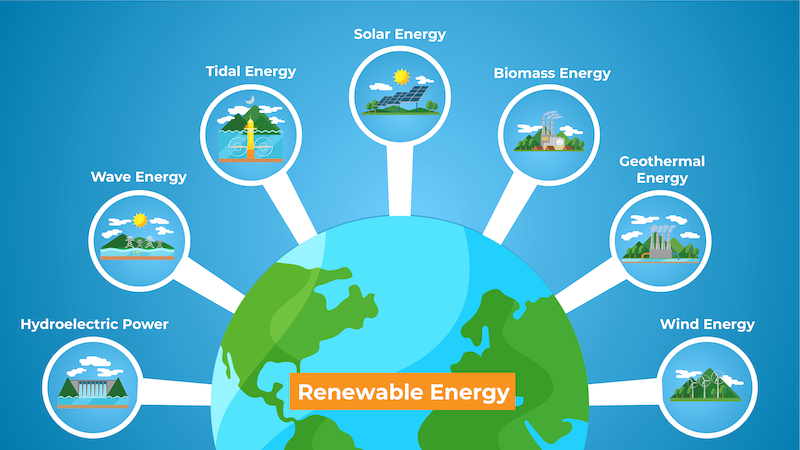
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are crucial in the transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy system. Various types of renewable energy sources are available, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore some of the most common ones:
Solar Energy
Solar energy is harnessed from the sun's rays using solar panels. It is a clean and abundant source of energy, making it one of the most popular renewable energy sources. The efficiency of solar energy depends on factors like weather conditions and location.
Wind Energy
Wind energy is generated by harnessing the power of wind through wind turbines. It is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly source of energy. The efficiency of wind energy depends on wind speed and consistency.
Hydro Energy
Hydro energy is derived from flowing water, typically through dams and turbines. It is a reliable source of energy, but it can have environmental impacts on aquatic ecosystems. The efficiency of hydro energy depends on water flow and elevation.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is produced by harnessing heat from the Earth's core. It is a consistent and reliable source of energy, but it is limited to areas with geothermal activity. The efficiency of geothermal energy is high due to its constant source of heat.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is generated from organic materials like wood, crops, and waste. It is a versatile source of energy, but it can have negative impacts on air quality and deforestation. The efficiency of biomass energy varies depending on the type of biomass used.Each type of renewable energy source has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of energy source depends on factors like location, resources, and environmental considerations.
Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable source of power that is harnessed through various technologies. One of the most common ways to capture solar energy is through the use of photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells.
Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are the building blocks of solar panels and are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that absorb photons from sunlight. When sunlight hits the cells, the photons knock electrons loose from their atoms, generating an electric current.
This direct current (DC) electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) by an inverter for use in homes, businesses, and the electric grid.
Solar Panels
Solar panels are composed of multiple photovoltaic cells connected together to form a larger unit. These panels are designed to capture sunlight efficiently and convert it into usable electricity. The panels are typically mounted on rooftops or in open spaces where they can receive maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day.
The design of solar panels allows for the easy installation and scalability of solar energy systems, making them a popular choice for residential and commercial applications.
Solar Energy Storage Technologies
Advancements in solar energy storage technologies have played a crucial role in overcoming the intermittent nature of solar power. Battery storage systems, such as lithium-ion batteries, are commonly used to store excess electricity generated by solar panels during the day for use during periods of low sunlight or at night.
These storage systems help ensure a reliable and continuous power supply from solar energy, making it a more viable and competitive source of renewable energy.
Innovations in Wind Energy Technology

Wind energy technology has seen significant advancements in recent years, leading to more efficient and reliable methods of generating electricity from wind. One of the key innovations in this field is the development of more sophisticated wind turbines that can harness the power of wind more effectively.
Generating Electricity using Wind Turbines
Wind turbines work by capturing the kinetic energy of the wind and converting it into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then used to spin a generator, which produces electricity. The blades of the turbine are designed to capture as much wind as possible and turn it into rotational energy.
Onshore vs. Offshore Wind Farms
Onshore wind farms are typically located on land and are more common than offshore wind farms, which are situated in bodies of water such as oceans or lakes. While onshore wind farms are easier and cheaper to build, offshore wind farms have the potential to generate more electricity due to stronger and more consistent wind speeds.
However, offshore wind farms are more expensive to construct and maintain.
Wind Energy Forecasting
Wind energy forecasting involves predicting the amount of energy that can be generated by wind turbines based on weather conditions. This is crucial for energy grid operators to balance the supply and demand of electricity. By accurately forecasting wind energy production, grid operators can better integrate wind power into the overall energy mix and reduce the reliance on fossil fuels.
Hydroelectric Power Generation

Hydroelectric power generation is a sustainable energy source that harnesses the power of flowing water to produce electricity. The process involves converting the kinetic energy of water into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy through turbines and generators.
Working Principle of Hydroelectric Power Plants
Hydroelectric power plants utilize the gravitational force of water to generate electricity. Water stored in a reservoir flows through a dam, which controls the release of water to maintain a steady flow. The water then passes through turbines connected to generators, where the mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy.
Role of Dams and Reservoirs
Dams play a crucial role in hydroelectric energy production by creating a reservoir where water can be stored. The reservoir acts as a water source for the power plant and helps regulate the flow of water to ensure a consistent supply.
Dams also control the release of water, allowing for increased power generation during peak demand periods.
Environmental Impacts and Benefits
Hydroelectric power has both environmental impacts and benefits. On one hand, the construction of dams and reservoirs can disrupt ecosystems, alter water flow patterns, and affect aquatic life. However, hydroelectric power is a clean and renewable energy source that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions and helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Additionally, hydroelectric power plants can provide a reliable source of electricity and contribute to energy security.
Geothermal Energy Systems
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses the heat from beneath the Earth's surface to generate electricity. This sustainable energy solution offers a constant and reliable power supply without relying on fossil fuels.
Geothermal Electricity Generation
Geothermal power plants use steam or hot water from underground reservoirs to drive turbines connected to generators, producing electricity. The heat extracted from the Earth's core is converted into usable energy, making geothermal power a clean and efficient alternative to traditional electricity generation methods.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps utilize the stable temperature of the ground to provide heating, cooling, and hot water for residential and commercial buildings. By circulating a fluid through underground pipes, the system absorbs heat in the winter and releases it in the summer, offering a more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solution for climate control.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction
Geothermal energy has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based power plants. By tapping into the Earth's natural heat, geothermal systems produce minimal carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants, contributing to a cleaner and greener energy landscape.
Biomass Energy Conversion Processes
Biomass energy conversion processes involve various methods to transform organic materials into usable energy. These processes play a crucial role in sustainable energy production and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Combustion
Combustion is a common method of converting biomass into energy, where organic materials are burned to release heat. This heat is then used to generate electricity or heat buildings. While combustion is a straightforward process, it can lead to air pollution if not properly controlled.
Gasification
Gasification is another method that converts biomass into a gas mixture called syngas. This syngas can be used to produce electricity, fuels, and chemicals. Gasification is considered more efficient than combustion and produces fewer emissions.
Fermentation
Fermentation is a biological process that involves breaking down organic materials using microorganisms to produce biofuels like ethanol. This method is commonly used in producing bioethanol from crops like corn and sugarcane.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Using biomass for energy production is considered sustainable as organic materials can be replenished through proper management. However, the environmental impact of biomass energy varies depending on factors like feedstock sourcing, processing methods, and emissions control. Sustainable practices and technologies are essential to minimize negative impacts on the environment.
Advancements in Bioenergy Technology
Recent advancements in bioenergy technology focus on improving the efficiency of biomass conversion processes. Technologies like integrated biorefineries, advanced biofuels, and biomass co-firing in existing power plants are being developed to enhance the overall performance and sustainability of bioenergy production.
These innovations aim to make bioenergy a more competitive and viable alternative to fossil fuels.
Energy Storage Solutions for Renewable Technologies
Energy storage plays a crucial role in the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. It allows for the efficient use of electricity generated from intermittent sources like solar and wind. Various energy storage technologies are utilized to store excess energy for later use, maintaining grid stability and reliability.
Battery Storage
Battery storage systems, such as lithium-ion batteries, are widely used for storing energy from renewable sources. They are highly efficient, scalable, and can be deployed at various scales, from residential to utility-level projects. These systems can provide fast response times and are ideal for short-duration energy storage needs.
Pumped Hydro Storage
Pumped hydro storage is one of the oldest and most common forms of energy storage. It involves pumping water to an elevated reservoir when energy is abundant and releasing it through turbines to generate electricity when needed. While it is highly efficient and has a long lifespan, it requires specific geographic conditions and significant initial investment.
Thermal Energy Storage
Thermal energy storage systems store heat or cold for later use, utilizing materials like molten salt or phase change materials. These systems are efficient for medium to long-duration storage needs, such as shifting energy demand to off-peak hours or storing excess heat from concentrated solar power plants.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Energy storage systems face challenges such as high costs, limited scalability, and technological limitations. However, ongoing research and development are focused on improving the efficiency, longevity, and cost-effectiveness of storage solutions. Future prospects include advancements in materials science, grid integration technologies, and regulatory frameworks to support the widespread adoption of energy storage in renewable energy systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, renewable energy technology stands at the forefront of addressing climate change and creating a more sustainable future for generations to come. By embracing these advancements and exploring new horizons, we pave the way for a cleaner, brighter tomorrow.
Clarifying Questions
How do photovoltaic cells work?
Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity by utilizing the photoelectric effect, where photons from sunlight dislodge electrons in the cells to generate an electric current.
What are the advantages of hydroelectric power generation?
Hydroelectric power is a clean and renewable energy source that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, provides reliable power generation, and can also help with flood control and irrigation.
What are the challenges of energy storage solutions for renewable technologies?
Some challenges include the intermittency of renewable sources like solar and wind, the cost of storage technologies, and the need for improved scalability and efficiency to meet increasing energy demands.